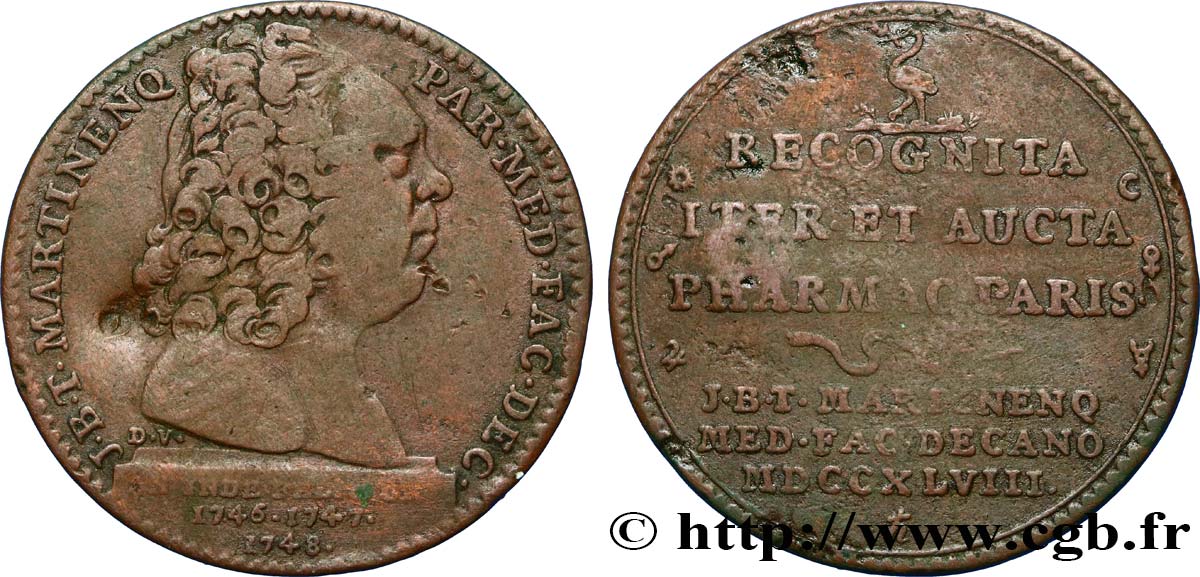
正面
正面的文字 J. B. T. MARTINENQ. PAR. MED. FAC. DEC. - AN. INDE. FELICIOR. 1746. 1747. 1748.
正面的说明书 Buste dénudé de Martinenq sur un socle portant un texte.
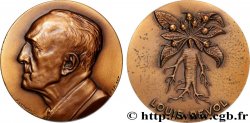
背面
背面的文字 RECOGNITA ITER ET AUCTA PHARMAC . PARIS - J. B. T. MARTINENQ. MED. FAC. DECANO. M. D. CC. XLVIII.
背面的说明书 légende en six lignes sous une cigogne, ponctuée d'un serpent et entourée de symboles alchimiques de métaux et de planètes.
背面的翻译 Pharmacie de Paris reconnue une seconde fois et aggrandie, sous Martinenq, de la faculté de médecine..
历史细节
PHARMACISTS - CHEMISTS - APOTHECARIES
Following the Muslims, European medieval pharmacy was enriched by chemical research. The common doctrine considered that diseases constituted morbid essences and that remedies acted as antidote. Also appeared in the 16th and 17th centuries. new remedies like arnica, valerian, cinchona. The corporation of apothecaries was united with that of grocers because sugar, rare in the Middle Ages, was considered more of a remedy than a food. Apothecaries began to be regulated by Charles VIII in 1484, then Louis XII separated apothecaries from grocers. Access to the profession of pharmacist was difficult, which did not prevent doctors in Molière's time from considering pharmacist-apothecaries as inferior. The first public school of pharmacy dates from 1576 and Louis XVI transformed it into a College of Pharmacy in 1777. Then, Bonaparte organized the first three national schools of pharmacy in Paris, Montpellier and Strasbourg. Finally, the arrival of synthetic substances after 1850 led to the development of modern chemical pharmacy..








 对产品描述纠错
对产品描述纠错 打印
打印 分享我的选择
分享我的选择 提问
提问 Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 产品介绍
产品介绍